| Home | Definitions | History | Chart | Calculation | Quiz |
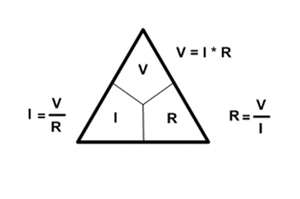
The equation I = V/R is known as "Ohmís Law". It states that the amount of steady current through a material is directly proportional to the voltage across the material divided by the electrical resistance of the material. The ohm (R), a unit of electrical resistance, is equal to that of a conductor in which a current (I) of one ampere is produced by a potential of one volt (V) across its terminals. These fundamental relationships represent the true beginning of electrical circuit analysis. The chart to the right shows the equations to figure out the missing value of R, I, or V accordingly.
The total resistance of two or more resistors connected in series is given by simply adding the individual values of the resistors to find the total sum:
To calculate the total resistance of a circuit that involves parallel resistors the following formula can be used:
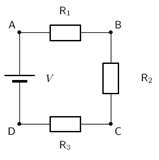
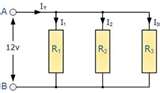
The diagrams below are examples of resistors in parallel circuits (left) and series circuits (right).